The sudden collapse of Silicon Valley Bank and the subsequent failures of Signature and First Republic focused attention on the US regional banking sector, as investors and policymakers sought other lenders who might share the same vulnerabilities. The KBW regional bank index is down nearly 30% since the beginning of March.
US Federal Reserve Chairman Jay Powell said this week he believed Monday’s sale of First Republic’s loans and assets to JPMorgan Chase was “an important step toward drawing the line during that severely stressed time.” adding that the deposit outflows that followed SVB’s demise “have really leveled off now.” But stock prices of some institutions remain deeply depressed.
The term regional bank covers a widespread and diverse group of institutions. They sit in the upper middle tier of a US banking sector that includes 5,000 lenders and ranges from JPMorgan, with assets of $3.7 trillionto tiny community banks with a branch.
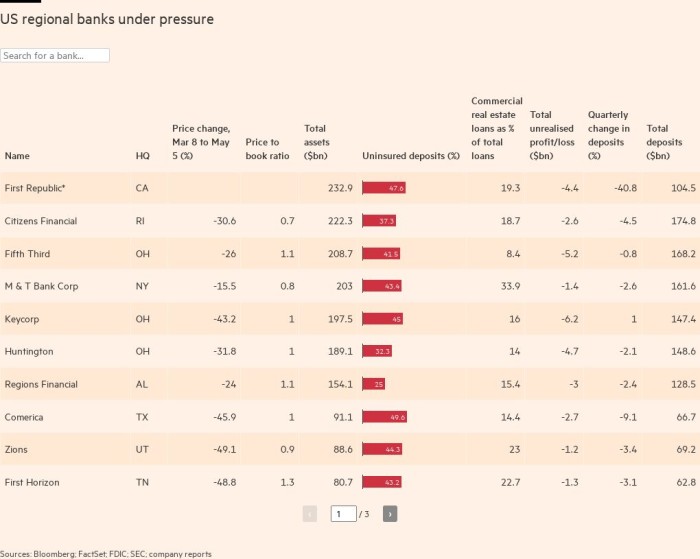
An analysis by the Financial Times looked at publicly traded banks with assets of $40bn to $400bn and highlighted those that saw the biggest drop in total return to shareholders since March 8, the day the SVB it really started to falter. We then compiled data that illuminates the perceived strength, size and business model of each institution.
While some banks have released updated data, the chart has used numbers since March 31, the last reporting date, in order to provide consistency on specific issues that have been cited as potential causes of financial stress.
Rapid outflows of deposits, particularly from accounts too large to be covered by the government’s insurance scheme, were the main reason the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation closed down SVB, Signature and First Republic.
SVB’s problems they were exacerbated by large unrealized losses on securities it held which suddenly crystallized as it needed liquidity to meet deposit outflows. Commercial real estate and loans to that sector are highly vulnerable to rapidly rising interest rates.
Price change — The percentage drop in the bank’s share price from March 8, two days before the SVB bankruptcy, to May 5. (set of facts)
Price-to-Book – The ratio compares a bank’s total market value to the value that says all of its loans, investments, and other assets, minus its debt, are worth. (set of facts)
Uninsured Deposits: The percentage of deposits at each bank above the insured level of $250,000 as of March 31 (FDIC and company reports)
Commercial Real Estate as a Percentage of Total Loans — The percentage of loans to owners of commercial real estate, such as office buildings or shopping malls, as of March 31. CRE is defined differently by different banks and we have mostly used the figures presented by the banks in their most recent earnings reports. FNB, Old National, Pinnacle Financial Partners and SouthState present figures for CRE and owner-occupied CRE, which we have combined in the table. PacWest included CRE and CRE multi-family, more commonly understood as condominiums, which we again combined. Cullen/Frost Bankers and First Republic did not report a figure, so we presented the most recent figure they filed with the FDIC.
Unrealized Losses – The value in billions of paper losses that banks estimate they have incurred on their bond portfolios as of 31 March. (FDIC)
Total deposits and change in quarterly deposits are as of March 31st. (FDIC)
*The First Republic has been shut down by the FDIC in early May, with most of its assets and deposits sold to JPMorgan. Silicon Valley Bank and Signature Bank were left out as both had gone bankrupt before reporting the March 31 numbers.
—————————————————-
Source link